GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
METALLURGY
The science and technology of isolation of pure metals from their ores and preparing them for practical use. The process includes-
- Mining - getting the ore out of ground
- Concentration - preparing for further treatment
- Reduction - to obtain the metals in zero oxidation state
- Refining - to obtain the pure metal
- Mixing with other metals - to form an alloy
MINERALS
Most metals are found in nature in the form of solid inorganic compounds called minerals. Names of minerals are based on the location of their discovery, the person who discovered them or some characteristics of the mineral.
ORE
The mineral from which the metal can be extracted economically. Hence all minerals can not be classified as ores. The most important ores are oxide,sulphide and carbonate minerals.
GANGUE OR MATRIX
The unwanted rocky,earthy or sandy materials almost always associated with the ores as impurities are called gangue or matrix.
FLUX AND SLAG
Flux is a substance added to the ores before heating which combines chemically with earthy impurities (gangue) and form a fusible mass known as slag .
Flux can be Acidic e.g.SiO2 (silica), Na2B4O7.10H2O (borax); Basic e.g. CaO, MgO ; or Neutral - neutral compounds, and they decrease the melting point and make the order conducting in an electrolytic cell e.g. CaF2, Na3AlF6, KF etc.
Slag consists mostly of molten silicates ,aluminates, phosphates, fluorides and another inorganic materials. The formation of slag is known as slagging.
CONCENTRATION OR DRESSING
The process of the removal of gangue or matrix from the ore is known as concentration. It is achieved by-
- Hand picking
- Gravity separation (hydraulic-washing )
- Magnetic separation
- Electrostatic separation
- Froth flotation process -for sulphide ores.
- Leaching
Froth flotation process - Finely divided ore is mixed with oil (pine oil, eucalyptus oil or camphor oil) and agitated with water containing a detergent (foaming agent). When air is bubbled through the mixture, the air bubbles are stabilised by the detergent .These adsorb mineral particles wetted with oil and rise to the surface. The earthy matter wetted by water settles down at the bottom.
Collectors - Which increase the non wettability of ore particles e.g. pine oil, xanthates and fatty acids.
Froth stabilizers - Which stabilise the froth e.g. cresoles and aniline.
Depressants - Depressants prevent the formation of froth eg NaCN, when added to ore containing ZnS and PbS form a complex with ZnS as and prevent it from forming froth. PbS is then easily separated from ZnS.
and prevent it from forming froth. PbS is then easily separated from ZnS.
Leaching - Leaching is the selective dissolution of the desired mineral leaving behind the impurities in a suitable dissolving agent eg bauxite when treated with strong solution of NaOH,dissolves leaving behind  .
.
Leaching is also employed in Ag ore and native gold.
CALCINATION
It is the heating of the ore in a suitable furnace in absence of air much below its melting point to cause decomposition and elimination of volatile products.
The process is generally applied to hydrated oxide or carbonate ores.
ROASTING
It is the heating of the concentrated ore in a suitable furnace strongly in presence of air with or without certain substances below the melting point which causes chemical reaction to expel volatile impurities eg oxides of S, As and Sb.
REDUCTION
After calcination or roasting, the metal oxides are reduced and impurities are removed as slag. Reduction and slagging take place together.
REMOVAL OF IMPURITIES AS SLAG
For acidic impurities viz. basic flux is added.
For basic impurities like MnO acidic flux is added.
REDUCTION OF OXIDES
DECOMPOSITION OF OXIDES BY HEATING
For thermally unstable oxide.
Hg is obtained from its sulphide ore cinnabar directly in the roasting step.
REDUCTION BY CARBON
Sn from oxide ore cassiterite SnO2 is obtained by heating with coke.
Zn from sulphide ore Zinc blende (ZnS).
Iron is obtained from oxide ore haematite (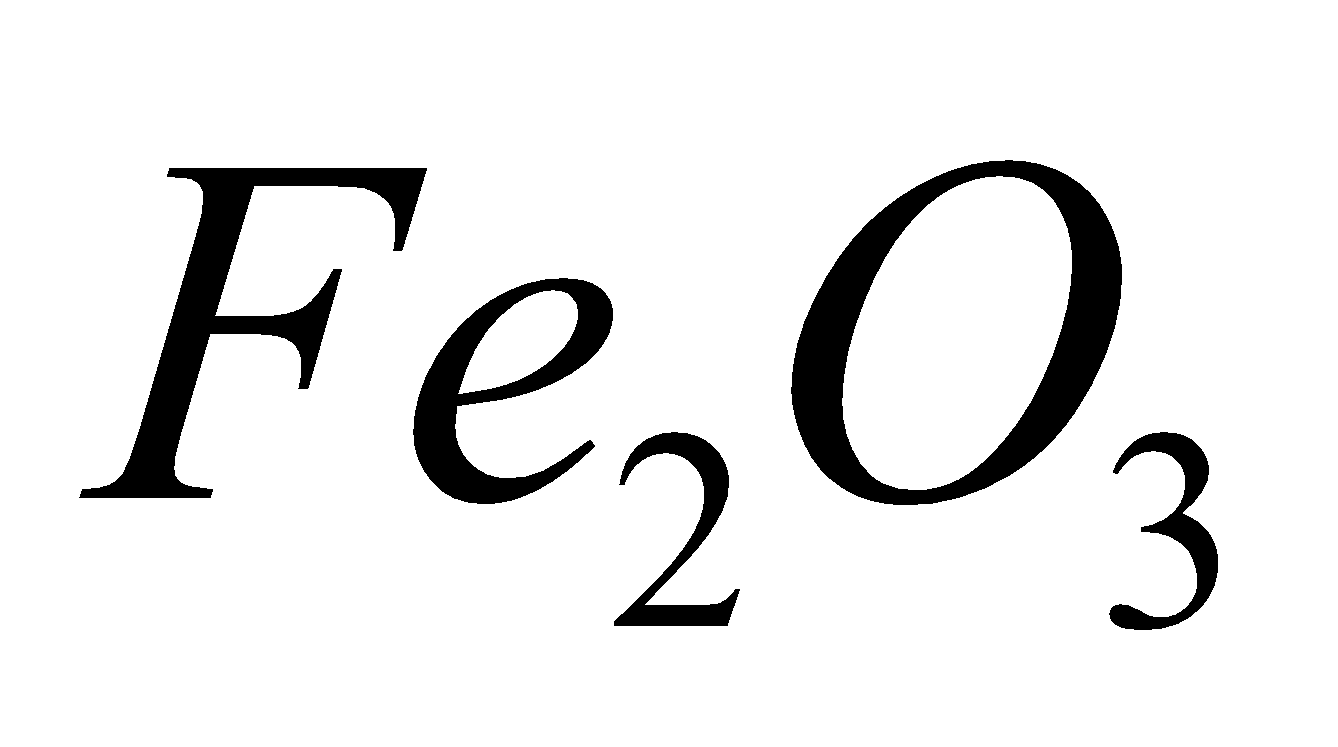 ).
).
REDUCTION BY H2 AND CO
REDUCTION BY OTHER METALS
e.g. Al and Mg
e.g. Al and Mg
SELF REDUCTION
Cu, Pb and Mg are obtained by self reduction in roasting.
ELECTROLYTIC REDUCTION
Oxides of very active metals like alkali or alkaline earth are not easily reduced by chemical reducing agents e.g. Na, Mg, Al etc. They are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
AMALGAMATION PROCESS
Ag and Au are obtained by leaching process using solution of KCN or NaCN to form argento cyanide or aurocyanide . Ag and Au is precipitated by adding Zn dust.
REFINING
The methods employed for the refining of metals are-
LIQUATION
Impurities present must be less fusible than the metal to be purified . Impure metal is placed on the sloping hearth of reverberatory furnace at a temperature just above the melting point of the metal . The pure metal flows down leaving behind the impurities . Sn ,Pb, Bi are purified by this method.
DISTILLATION
Zn and Hg are purified by distillation under reduced pressure provided the impurities are non volatile.
FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLISATION (ZONE REFINING)
Impure metal rod is heated with the help of circular heater at one end. The metal melts and on cooling the pure metal gets solidified while impurities pass on into the molten zone. The process is repeated twice or thrice to get the pure metal.
POLLING
The molten metal is stirred with green poles of wood, which liberates gas like methane. The latter reduces any oxide present in the metal eg CuO in the blister copper is reduced to copper.
ELECTROLYTIC REFINING
The blocks of impure metal form the anode and pure metal form the cathode. Aqueous solution of appropriate salt is then electrolysed. On electrolysis at a suitable voltage the pure metal is deposited at cathode.
Cu, Sn, Ag, Pb, Cr, Ni are refined by this process.
VAPOUR PHASE REFINING
Metal is removed as volatile compound which is then decomposed by heating to get pure metal. e.g.
Mond’s process
Ni is purified by this process.
Van Arkel process
Zr, Hf , Si,Ti and Be are refined by this process.
CUPELLATION
This is the method of purifying silver containing lead as impurity. Impure silver is heated in a shallow (Cupel) which is made of bone ash under blast of air. Lead is easily oxidised and carried away by blast air. There are several chromatographic techniques such as gas chromatography, paper chromatography, etc.
DESILVERISATION OF LEAD
Lead obtained from galena (PbS) contains impurities of silver, removal of which is called desilverisation .The processes employed are-
Parke’s process -Lead containing silver is melted in iron pots and 1% Zn is added then cooled. Zn -Ag alloy solidifies and being light floats over molten lead and removed.
Pattison’s process - Lead containing less than 2.5% of Ag melts at lower temperature than lead. Thus, when an alloy of Pb-Ag containing more lead is melted then allowed to cool slowly, pure lead separates.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS
It is based on the preferential adsorption of different compounds on an adsorbent. The mixture is put in the liquid or gaseous medium which is moved through the adsorbent. The different compounds are adsorbed at different levels on adsorbent in column chromatography and recovered by using suitable solvent (eluent). The common adsorbent as Al2O3 or SiO2 (silica). The least adsorbed component is recovered first. The method is very useful for purification of elements available in minute quantities.
SOME IMPORTANT TERMS USED IN METALLURGY
PYROMETALLURGY
In this process decomposition of the minerals and the extraction of the metal is brought about in dry state at high temperature by the action of heat. The steps employed are-
- Calcination
- Roasting
- Smelting
- Refining
Smelting is melting process that causes the materials to separate into two or more layers.
Two important kinds of layers are slag and molten metal. Iron is obtained by pyrometallurgy.
HYDROMETALLURGY
Extraction of metals from ores using aqueous solution. It includes-
- Leaching
- Reduction
Ag and Au are extracted by this process.
ELECTROMETALLURGY
Electrometallurgy is the process of obtaining metals through electrolysis. The electropositive metals are obtained by this method e.g. Na, Mg etc.
AMALGAMATION
In this process the metal is extracted by using mercury. Most of the metals dissolve in Hg to form amalgams which when distilled in iron retorts leave behind free metal and Hg distills over
Ag, Au, Pt form amalgam.
THERMIT
It is mixture of  (3 parts ) and Al powder (1part) when ignited with the help of barium peroxide,
(3 parts ) and Al powder (1part) when ignited with the help of barium peroxide, 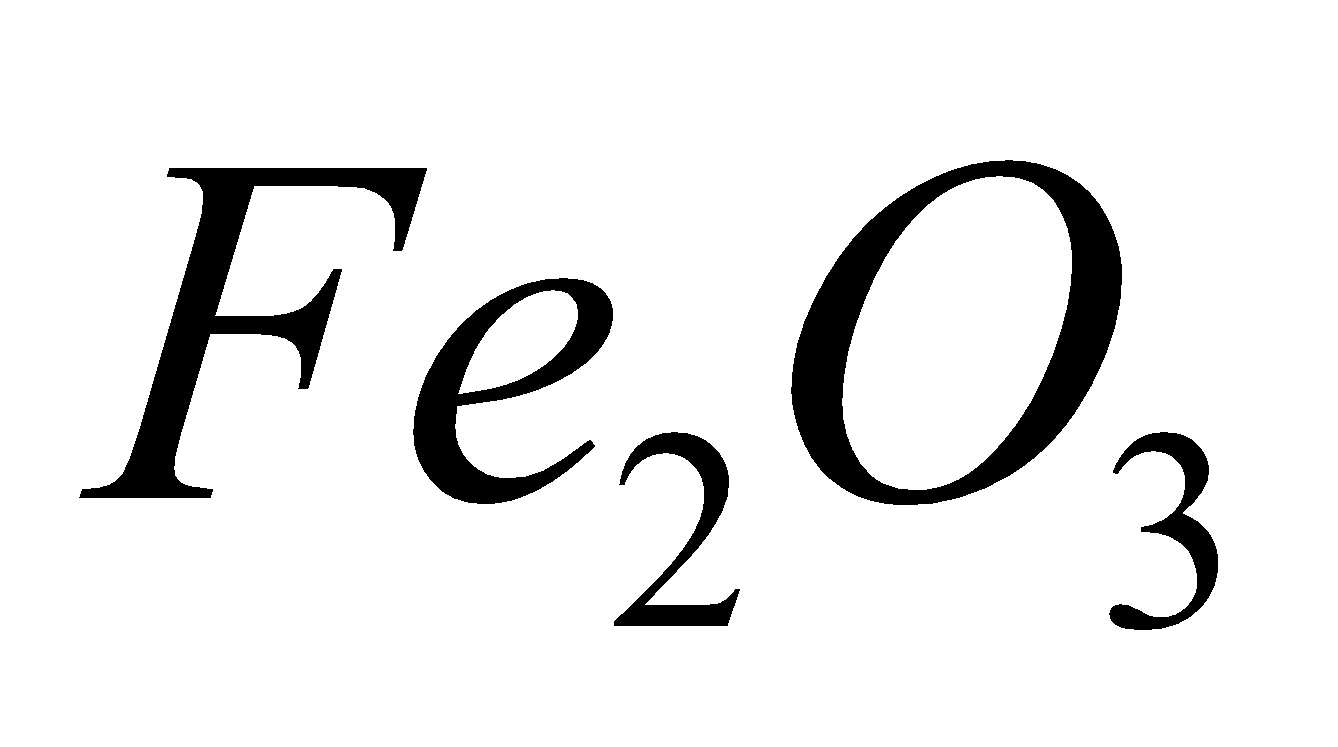 is reduced to iron and an enormous amount of heat is produced due to exothermic nature of the reaction.
is reduced to iron and an enormous amount of heat is produced due to exothermic nature of the reaction.
The molten is utilised for welding and the process is known as thermit welding known as Goldschmidt Aluminothermic process.
REFRACTORY MATERIALS
The substance capable of withstanding at very high temperature without undergoing any deformation is called refractory material.
Acidic refractories -silica, quartz and sandstone
Basic refractories - lime ,dolomite and magnesite
Neutral refractories - chromite, bone ash and graphite.
MATTE OR REGULUS
Artificially obtained sulphides are known as matte or regulus e.g. in extraction of copper.
SULPHATING ROASTING
It is partial oxidising roasting. Roasting of galena gives mixture of lead oxide and lead sulphate
CHLORINATING ROASTING
Silver ores mixed with common salt when heated in presence of air, the chloride is obtained.
BESSEMERISATION
The oxidation of impurities by passing the hot blast of air through molten metal in bessemer converter is called bessemerisation . Pig iron and copper are purified by this method.
SINTERING
The conversion of small pieces of a substances into larger one by partial fusion is known as sintering.
PULVERISATION
The conversion of large pieces of a substance into small fine pieces or powder is known as pulverisation.
ANODIZING
The process of forming an oxide coating on metal surface by making it an anode by electrolytic method in called anodizing.
MODE OF EXTRACTION OF SOME METALS
- Metals obtained by electrolytic reduction are - Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca , Al, Sr, Ba
- Metals obtained by reduction of oxides by carbon are - Zn from ZnO, Sn from SnO2.
- Metals obtained by reduction of oxides by thermite process, (Alumino thermic process) are Cr from Cr2O3, Mn from Mn3O4.
- Metals obtained by air reduction method are - Hg from HgS, Pb from PbS.
- Metals obtained by precipitation method are - Ag ,Au
- Metals obtained by reduction with Co, Fe
- Metals obtained by reduction with water gas are - Ni
ALLOYS
Alloys contain more than one element and have the characteristics of metals.
- Pure metals and alloys have different physical properties.
- Solution alloys are homogeneous mixtures and they are of two types
- Substitutional alloys (Solute atoms take the positions of solvent atom)
- Interstitial alloys (Solute atoms occupy interstitial sites)
- Heterogeneous alloys - Components are not dispersed uniformly e.g. pearlite steel
RELATIVE ABUNDANCE
Abundance of elements in the earth’s crust (by weight)
Abundance of elements in the earth’s crust (in terms of number of atoms per 100 atoms)
THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES OF METALLURGY
Theory of metallurgical transformations can be interpreted by Gibb’s free energy change at any specified temp.
where,  H = enthalpy change and
H = enthalpy change and
K = equilibrium constant at temp. T
The reducing agent is oxidised and metal oxide is reduced. The role of reducing agent is to provide  Gº negative.
Gº negative.
During reduction the metal oxide decomposes.
The reducing agent (C or CO) is oxidised
If net DG of two possible reactions (Reduction/Oxidation) is negative, the overall reaction will occur.
H.J.T. Ellingham diagram (plots of 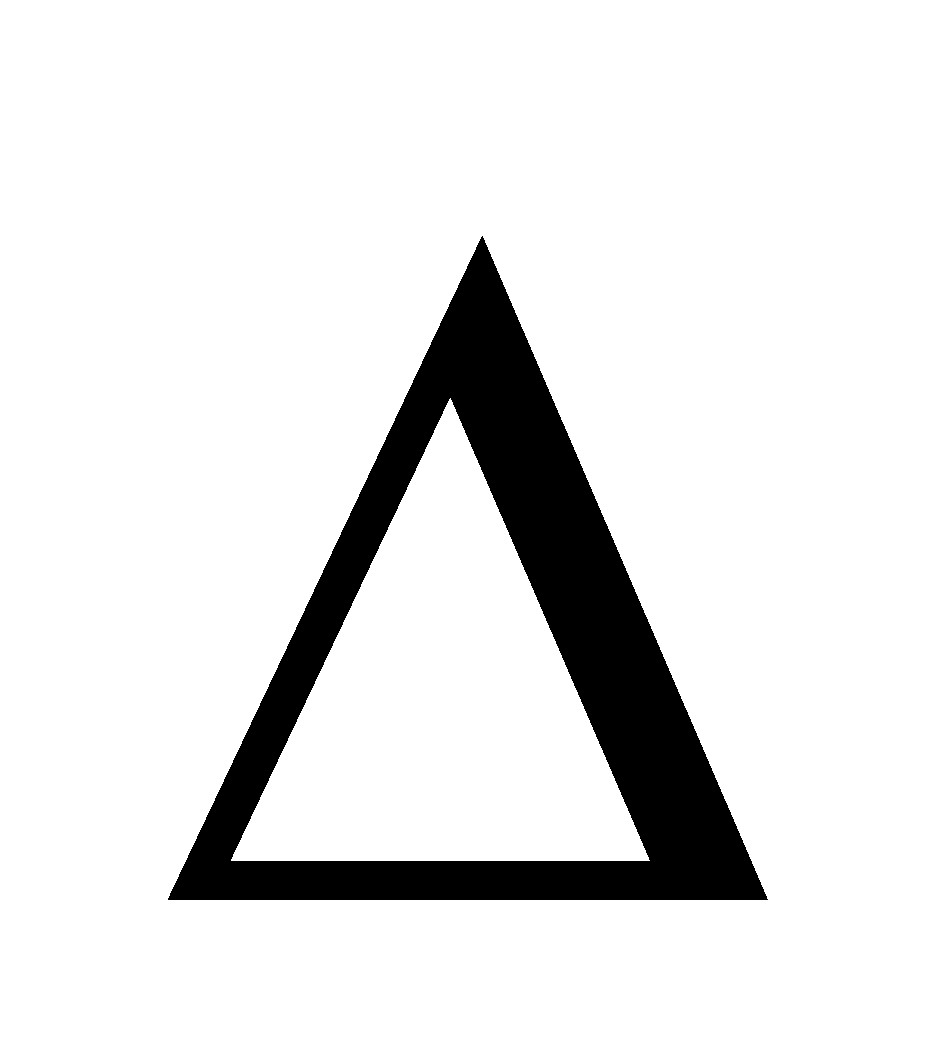 G Vs T) provides a sound basis for considering the choice of reducing agent in the reduction of oxides.
G Vs T) provides a sound basis for considering the choice of reducing agent in the reduction of oxides.
Fig. Gibbs energy ( Gº) vs T plots (schematic) for formation of some oxides (Ellingham diagram)
Gº) vs T plots (schematic) for formation of some oxides (Ellingham diagram)
When alumina is reduced by magnesium, the two equations are
DG becomes ZERO at the point of intersection of the Al2O3 and MgO curves (marked “A”). Above this point the magnesium can reduce alumina.
Note: Although thermodynamically feasible the magnesium metal, is not used for the reduction of aluminas. The temperature required would be so high and the process would be technologically difficult and uneconomic.
LIMITATIONS OF ELLINGHAM DIAGRAM
- It fails to predict the kinetics of reduction processes i.e. how fast it could be
- When the reactant/product are solid
G° cannot be interpreted by the equation
G° = – RT log K
EXTRACTION OF IRON FROM ITS OXIDES
The two simple reactions are-
Adding the two reactions, we get
FeO(s) + C(s) Fe(s/l) + CO(g)
The resultant  G is –ve above 1073K (approx).
G is –ve above 1073K (approx).
If the metal is obtained in liquid state the reduction becomes easier. (entropy increases and DG decreases).










