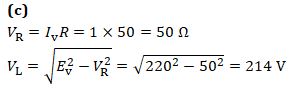JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of concepts.
Q1. The peak value of an alternating emf E given by E=E0cosωt
is 10 V and frequency is 50 Hz. At time t=(1/600) s, the instantaneous value of emf is
Q3. An ac voltage is represented by E=220 √2cos(50 π)t. How many times will the current become zero in 1 s?
Q4. In series LCR circuit voltage drop across resistance is 8 V, across inductor is 6 V and across capacitor is 12 V. Then
Q5. Using an ac voltmeter, the potential difference in the electrical line in a house is read to be 234 V. If the line frequency is known to be 50 cycles/second, the equation for the line voltage is
Q6. An alternating voltage E=50 √2 sin(100 t) V is connected to a 1 μ F capacitor through an ac ammeter. What will be the reading of the ammeter?
Q7. In LCR circuit current resonant frequency is 600 Hz and half power points are at 650 and 550 Hz. The quality factor is
Q9. In the circuit shown in Fig, XC=100 Ω,XL=200 Ωand R=100 Ω. The effective current through the source is
Q10. A 220-V, 50 Hz ac generator is connected to an inductor and a 50 Ω resistance in series. The current in the circuit is 1.0 A. What is the pd across inductor?