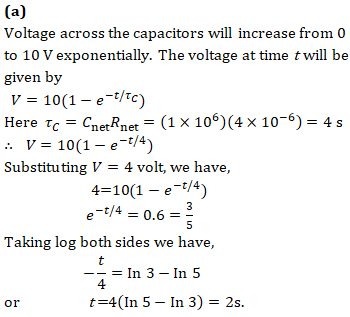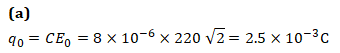JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of concepts.
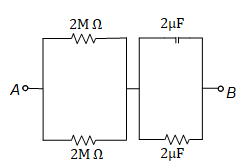
Q1. At time t = 0, a battery of 10 V is connected across points A and B in the given circuit. If the capacitors have no charge initially, at what time (in second) does the voltage across them become 4 V?(Take ln 5 = 1.6, ln 3 = 1.1)
Q2. An8 μF capacitor is connected across a 220 V, 50 Hz line. What is the peak value of charge through the capacitor?
Q3. What reading would you expect of a square-wave current, switching rapidly between +0.5 A and -0.5 A, when passed through an ac ammeter?
Q4. A capacitor of 10 μF and an inductor of 1 H are joined in series. An ac of 50 Hz is applied to this combination. What is the impedance of the combination?
Q5. Two resistors are connected in series across as 5 V rms source of alternating potential. The potential difference across 6 Ω resistor is 3 V. If R is replaced by a pure inductorL of such magnitude that current remains same, then the potential difference across L is
Q8. A direct current of 5 A is superimposed on an alternating current I=10 sinωt flowing through a wire. The effective value of the resulting current will be
Q9. The rms value of an ac of 50 Hz is 10 A. The time taken by an alternating current in reaching from zero to maximum value and the peak value will be
Q10. An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency ω and fixed amplitude V0 is connected in series with a capacitance C and an electric bulb of resistance R (inductance zero). When ω is increased