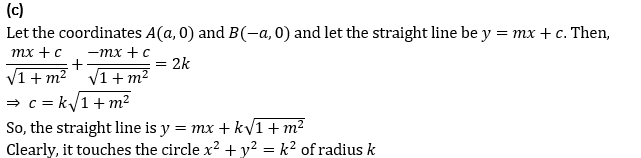In JEE exams, Conic section is one of the most important topic of Mathematics that comes under Coordinate Geometry, it has total of 15 percent weightage out of which 6% questions are asked in JEE mains and 9% in Advance.
Q2. Minimum radius of circle which is orthogonal with both the circles x2+y2-12x+35=0 and x2+y2+4x+3=0 is
Q3. If one of the diameters of the circle x2+y2-2x-6y+6=0 is a chord to the circle with centre (2, 1), then the radius of the circle is
Q4. Let any double ordinate PNP' of the hyperbola x2/25+y2/16=1 be produced on both sides to meet the asymptotes in Q and Q', then PQ∙P'Q is equal to
Q5. If (0,6)and (0,3) are respectively the vertex and focus of a parabola, then its equation is
Q6. P is a point on the hyperbola x2/a2 -y2/b2 =1, N is the foot of the perpendicular from P on the transverse axis. The tangent to the hyperbola at P meets the transverse axis at T. If O is the centre of the hyperbola, the OT. ON is equal to
Q7. If the locus of middle of point of contact of tangent drawn to the parabola y2=8x and foot of perpendicular drawn from its focus to the tangents is a conic then length of latus rectum of this conic is
Q8. Consider the parabola y2=4x. A≡(4,-4) and B≡(9,6) be two fixed points on the parabola. Let ‘C’ be a moving point on the parabola between A and B such that the area of the triangle ABC is maximum, then coordiante of ‘C’
Q9.If O is the origin and OP,OQ are the tangents from the origin to the circle x2+y2-6x+4y+8=0, then circumcenter of the triangle OPQ is
Q10.A straight line moves such that the algebraic sum of the perpendicular drawn to it from two fixed points is equal to 2k. Then , the straight line always touches a fixed circle of radius