JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get
a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance
examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a
way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to
further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic
by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other
two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in
such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of
concepts.
Gravitation is an easy to understand and a highly scoring topic. It
might have a 1% weightage in the entire JEE Physics portion but do not
neglect. You can practice these questions on regular basis to know what
are the important points to remember at the moment when
gravitation question comes.
Q2.The percentage change in the acceleration of the earth
towards the Sun from a total eclipse of the Sun to the point
where the Moon is on a side of earth directly opposite to the
Sun is
Q3.The two planets with radii R1,R2
have densities ρ1,ρ2, and atmospheric
pressure p1 and p2, respectively.
Therefore, the ratio of masses of their atmospheres,
neglecting variation of g and ρ within the limits of
atmosphere, is
Q4.If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface, the change in the potential energy of an object of mass m raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius R of the earth is
Q5.The value of g at a particular point is 10 m
s-2. Suppose the earth shrinks uniformly to half of
its present size without losing any mass. The value of g at
the same point (assuming that the distance of the point from
the centre of the earth does not change) will now be
Q6.If g is acceleration due to gravity on the earth's
surface, the gain in the potential energy of an object of mass
m raised from the surface of earth to a height equal to the
radius R of the earth is
Q7.If W1,W2 and W3 represent
the work done in moving a particle from A to B along three
different paths 1, 2 and 3, respectively, (as shown in the
figure) in the gravitational field of a point mass m, find the
correct relation between W1,W2 and W3
Q8.The maximum vertical distance through which a fully
dressed astronaut can jump on the earth is 0.5 m. If mean
density of the Moon is two-third that of the earth and radius
is one quarter that of the earth, the maximum vertical
distance through which he can jump on the Moon and the ratio
of the time of duration of the jump on the Moon to hold on the
earth are
Q9. A satellite of mass m is revolving around the earth at
height R (radius of the earth) from the earth's surface. Its
potential energy will be
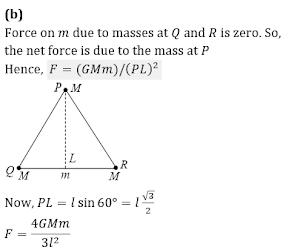
Q10.Three particles, each of mass M, are placed at the three
corners of an equilateral triangle of side l. What is the
force due to this system of particles on another particle of
mass m placed at the midpoint of any side?