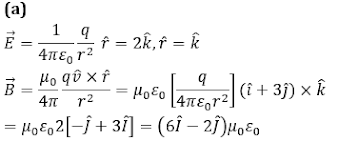MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM - 12
Dear Readers,
JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of concepts..
Q1. A particle of charge per unit mass α is released from origin with velocity v =v_0 i ̂ in a magnetic field
B =-B_0 k ̂ for x≤√3/2 v_0/(B_0 α)
And B =0 for x>√3/2 v_0/(B_0 α)
The x-co-ordinate of the particle at time t(>π/(3B_0 α)) would be
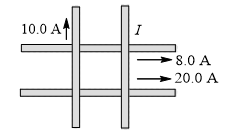
Q2. Four very long, current carrying wires in the same plane intersect to form a
square 40.0 cm on each side, as shown in figure. Find the magnitude and
direction of the current I so that the magnetic field at the centre of the
square is zero
Q3. In Fig., there is a uniform conducting structure in which each small square has
side a. The structure is kept in a uniform magnetic filed B. Then the magnetic
force on the structure will be
Q4. A particle is moving with velocity v =i +3j and it produces an electric
filed at a point given byE =2k ̂. It will produce magnetic field at that point
equal to (all quantities are in S.I. units)
Q5. A charged particle of specific charge (charge/ mass) α is released from origin at time t=0 with velocity v =v_0 (i ̂+j ̂) in uniform magnetic fieldB =B_0 i ̂. Coordinates of the particle at time t=π(B_0 α) are
Q6. In a moving coil galvanometer, we use a radial magnetic feild so that the galvanometer scale is
Q7. A positively charged disk is rotated clockwise as shown in figure. The direction of the magnetic field at point A in the plane of the disk is