JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of concepts.</.
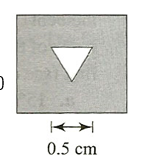
Q1. A parallel beam of light falls axially on a thin converging lens of focal length 20 cm. The emergent light falls or a screen placed 30 cm beyond the lens. An opaque plate with a triangular aperture, side 1 cm, is in contact with the lens. (see figure)Which one of the following diagrams best shows to appearance of the patch of light seen on the screen?
Solution
The image on the screen is real and inverted
The size of the image on the screen has aperture size given by
Size =1.0 (10/20)=0.5 cm Hence, the path of light on the screen is best represented by diagram (d)
The image on the screen is real and inverted
The size of the image on the screen has aperture size given by
Size =1.0 (10/20)=0.5 cm Hence, the path of light on the screen is best represented by diagram (d)
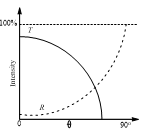
Q2.A light ray travelling in glass medium is incident on glass-air interface at an angle of incidenceθ. The reflected (R) and transmitted (T) intensities, both as function of θ, are plotted. The correct sketch is
Solution
After critical angle reflection will be 100% and transmission is 0 %. Options (b) and (c) satisfy this condition.
But option (c) is the correct option.
Because in option (b) transmission is given 100% at θ = 0°, which is not true ∴ Correct answer is (c).
After critical angle reflection will be 100% and transmission is 0 %. Options (b) and (c) satisfy this condition.
But option (c) is the correct option.
Because in option (b) transmission is given 100% at θ = 0°, which is not true ∴ Correct answer is (c).
Q3. A concave mirror is placed on a horizontal table with its axis directed vertically upward. Let O be the pole of the mirror and C its center of curvature. A point object is placed at C. It has a real image, also located at C. If the mirror is now filled with water, the image will be
Q4. Two identical glass (μ_g=3/2) equiconvex lenses of focal length f are kept in contact. The space between the two lenses is filled with water (μ_w=4/3). The focal length of the combination is
Q5. A glass sphere of radius R=10 cm is kept inside water. A point object O is placed at 20 cm from A as shown in figure. Find the position and nature of the image when seen from other side of the sphere. Given μ_g=3/2 and μ_w=4/3
Q6. A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5, has both surfaces of same radius of curvature R. On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a
Solution
f_l/f_a =( _a μ_g-1)/( _l μ_g-1)=(1.5-1)/(1.5/1.75-1)=-(1.75×0.50)/0.25=-3.5
∴f_l=-3.5 f_a⇒f_l=+3.5R [∵f_a=R]
Hence on immersing the lens in the liquid,
it behaves as a converging lens of focal length 3.5 R
f_l/f_a =( _a μ_g-1)/( _l μ_g-1)=(1.5-1)/(1.5/1.75-1)=-(1.75×0.50)/0.25=-3.5
∴f_l=-3.5 f_a⇒f_l=+3.5R [∵f_a=R]
Hence on immersing the lens in the liquid,
it behaves as a converging lens of focal length 3.5 R
Q7. A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror as shown in figure Determine the length of reflected path of light on the screen ∑
Q8.The critical angle for light going from medium X into medium Y is θ. The speed of light in medium X is v. The speed of light in medium Y is
Q9. A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism P? Additional prisms Q and R of identical shape and of the same material as P are now added as shown in figure. The ray will suffer:
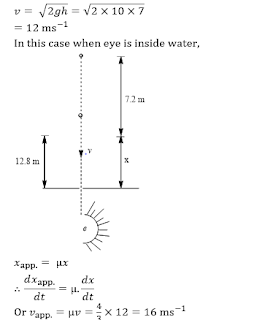
Q10. A ball is dropped from a height of 20m above the surface of water in a lake. The refractive index of water is4/3. A fish inside the lake, in the line of fall of the ball, is looking at the ball. At an instant, when the ball is 12.8 m above the water surface, the fish sees the speed of ball as