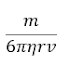JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of concepts.
Q1. The dimension of self-induction are
Q3. If force F, acceleration a, and time T are taken as the fundamental physical quantities, the dimensions of length on this system of units are
Solution
(d)
A T2 = L T-2 × T2 = [M0 L T0]
A T2 = L T-2 × T2 = [M0 L T0]
Q4. The heat generated in a circuit is given by Q=I2Rt, where I is current, R is resistance, and t is time. If the percentage errors in measuring I,R, and t are 2%, 1%, and 1%, respectively, then the maximum error in measuring heat will be
Solution
(d)
Required error is 2 × 2% + 1% + 1%, i.e., 6%
Required error is 2 × 2% + 1% + 1%, i.e., 6%
Q5. A student performs an experiment to determine the Young’s modulus of a wire, exactly 2 m long, by Searle’s method. In a particular reading, the student measures the extension in the length of the wire to be 0.8 mm with an uncertainty of ± 0.05 mm at a load of exactly 1.0 kg. The student also measures the diameter of the wire to be 0.4mm with an uncertainty of ± 0.01 mm. Take g=9.8 ms-2 (exact). The Young’s modulus obtained from the reading is
Q6. A spherical body of mass m and radius r is allowed to fall in a medium of viscosity η. The time in which the velocity of the body increases from zero to 0.63 times the terminal velocity (v) is called time constant (τ). Dimensionally τ can be represented by
Q7. Using mass (M), length (L), time (T), and electric current (A) as fundamental quantities, the dimensions of permittivity will be