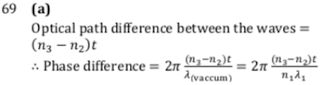JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get
a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance
examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a
way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to
further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic
by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other
two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in
such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of
concepts.
.
Q1. To produce a minimum reflection of wavelengths near the middle of visible spectrum (550 nm) how thick should a coating of MgF2(𝜇 = 1.38) be vacuum-coated on a glass surface?
Q2.Two light waves having the same wavelength 𝜆 in vacuum are in phase initially. Then, the first ray travels a path of length 𝐿1 through a medium of refractive index 𝜇1. The second ray travels a path of length 𝐿2 through a medium of refractive index 𝜇2. The two waves are then combined to observe interference effects. The phase difference between the two, when they interfere, is
Q3. Two thin films of the same material but different thickness are separated by air. Monochromatic light is incident on the first film. When viewed normally from point 𝐴, the second film appears dark
Q3. From point 𝐵, on normal viewing
Q4. Two waves of light in air have the same wavelength and are initially in phase. They then travel through plastic layers with thickness of 𝐿1 = 3.5 mm and 𝐿2 = 5.0 mm and indices of refraction 𝑛1 = 1.7 and 𝑛2 = 1.25 as shown in the figure. The rays later arrive at a common point. The longest wavelength of light for which constructive interference occurs at the point is
Q5.In YDSE, when a glass plate of refractive index 1.5 and thickness 𝑡 is placed in the path of one of the interfering beams (wavelength 𝜆), intensity at the position where central maximum occured previously remains unchanged. The minimum thickness of the glass plate is
Q6. The wavefront of a light beam is given by the equation 𝑥 + 2𝑦 + 3𝑥 = 𝑐 (where 𝑐 is arbitrary constant), then the angle made by the direction of light with the 𝑦-axis is
Q7.
In figure, a parallel beam of light is incident on the plane of the slits of a Young’s double-slit experiment. Light incident on the slit 𝑆1 passes through a medium of variable refractive index 𝜇 = 1 + 𝑎𝑥 (where ‘𝑥’ is the distance from the plane of slits as shown), up to a distance ‘𝑙’ before falling on 𝑆1. Rest of the space is filled with air. If at ‘𝑂’ a minima is formed, then the minimum value of the positive constant 𝑎 (in terms of 𝑙 and wavelength ‘𝜆’ in air) is
Q8.In a double-slit experiment, two parallel slits are illuminated first by light of wavelength 400 nm and then by light of unknown wavelength. The fourth-order dark fringe resulting from the known wavelength of light falls in the same place on the screen as the second-order bright fringe from the unknown wavelength. The value of unknown wavelength of the light is
Q9.In a YDSE shown in figure, a parallel beam of light is incident on the slits from a medium of refractive index 𝑛1. The wavelength of light in this medium is 𝜆1. A transparent slab of thickness ‘𝑡’ and refractive index 𝑛3 is put in front of one slit. The medium between the screen and the plane of the slits is 𝑛2. The phase difference between the light waves reaching point ‘𝑂’ (symmetrical, relative to the slits) is
Q10. A long horizontal slit is placed 1 mm above a horizontal plane mirror. The interference between the light coming directly from the slit and that after reflection is seen on a screen 1 m away from the slit. If the mirror reflects only 64% of the light falling on it, the ratio of the maximum to the minimum intensity in the interference pattern observed on the screen is