JEE Advanced paper is considered to be one of the toughest entrance exams in India. Moreover, this Physics is considered the toughest subject because it is the most application-based. The student needs to get the basics right and then move on to mastering advanced concepts. Waves consist of nearly about 4-5 % of marks in the Physics section.
Q1. Spherical sound waves are emitted uniformly in all directions from a point source. The variation in sound level SL as a function of distance 'r' from the source can be written as, Where a and b are positive constants
Q2. Two separated sources emit sinusoidal travelling waves but have the same wavelength λ and are in phase at their respective sources. One travels a distance l1 to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance, l2. The amplitude is minimum at the observation point, if l1 - l2 is an
Solution
(c)
For destructive interference, path difference must be equal to an odd integral multiple of λ/2
(c)
For destructive interference, path difference must be equal to an odd integral multiple of λ/2
Q3. If x = a sin[ωt+π/6] and x' = a cos ωt , then what is the phase difference between the two waves?
Q4. A thin plane membrane separates hydrogen at 7°C from hydrogen at 47°C, both being at the same pressure. If a collimated sound beam travelling from cooler gas makes an angle of incidence of 30° at the membrane, the angle of refraction is
Q5. A police car with a siren of frequency 8 kHz is moving with uniform velocity 36 km/h towards a tall building which reflects the sound waves. The speed of sound in air is 320 m/s. the frequency of the siren heard by the car driver is
Q6. A transverse sinusoidal wave is generated at one end of a long horizontal string by a bar that moves the end up and down through a distance by 2.0 cm. The motion of bar is continuous and is repeated regularly 125 times per second. If the distance between adjacent wave crests is observed to be 15.6 cm and the wave is moving along positive x-direction, and at t = 0 the element of the string at x = 0 is at means position y = 0 and is moving downward, the equation of the wave is best described by
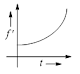
Q7. A source of frequency ‘f’ is stationary and an observer starts moving towards it at t = 0 with constant small acceleration. Then the variation of observed frequency ‘f’ registered by the observer with time is best represented as
Q8. A progressive wave is given by
y = 3sin2π[ (t ⁄ (0.04) - (x ⁄ (0.01) ]
Where x,y are in cm and t in s. The frequency of wave and maximum accelerartion will be:
Where x,y are in cm and t in s. The frequency of wave and maximum accelerartion will be:
Q10. The difference between the apparent frequencies of a source of sound as perceived by a stationary observer during its approach and recession is 2 % of the actual frequency of the source. If the speed of sound is 300 m/s the speed of source is