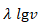Work power energy is the most important chapter when it comes to mechanics, for JEE (Advanced). The chapter is quite tricky and takes a lot of time and devotion on your part to understand and master. But this chapter is a complete gold medal for almost all the questions of the mechanics can be solved by the work power energy approach if you master this topic..
Q2.
A pump motor is used to deliver water at a certain rate from a given pipe. To obtain n times water from the same pipe in the same time, by what amount should the power of the motor be increased?
Q3. A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that its centripetal acceleration a_c is varying with time t as ac=k^2 rt^2, where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particle by the forces acting on it is
Q4.
Work done in time t on a body of mass m, which is accelerated from rest to a speed v in time t1 as a function of time t, is given by
Q5.In the above questions, if equal forces are applied on two springs, then
Solution
Spring Q has lesser force constant thanP. So Q will develop less restoring force than P. As a result, Q wi8ll suffer more extension. Since force is same in both the cases, more work will be done on Q
Q6.
In the above question, the maximum power delivered by the agent in pulling up the rope is
Q8.
A car drives along a straight level frictionless road by an engine delivering constant power. Then velocity is directly proportional to
Solution
Q9.
An automobile weighing 1200 kg climbs up a hill that rises 1 in 20. Neglecting frictional effects, the minimum power developed by the engine is 9000 W. If g=10 ms^(-2), then the velocity of the automobile is
Q10.
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are v and 2v respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at A ,these two particles will again reach The point A?